Elecrified & Hybrid Honda Models at Southeastern Honda
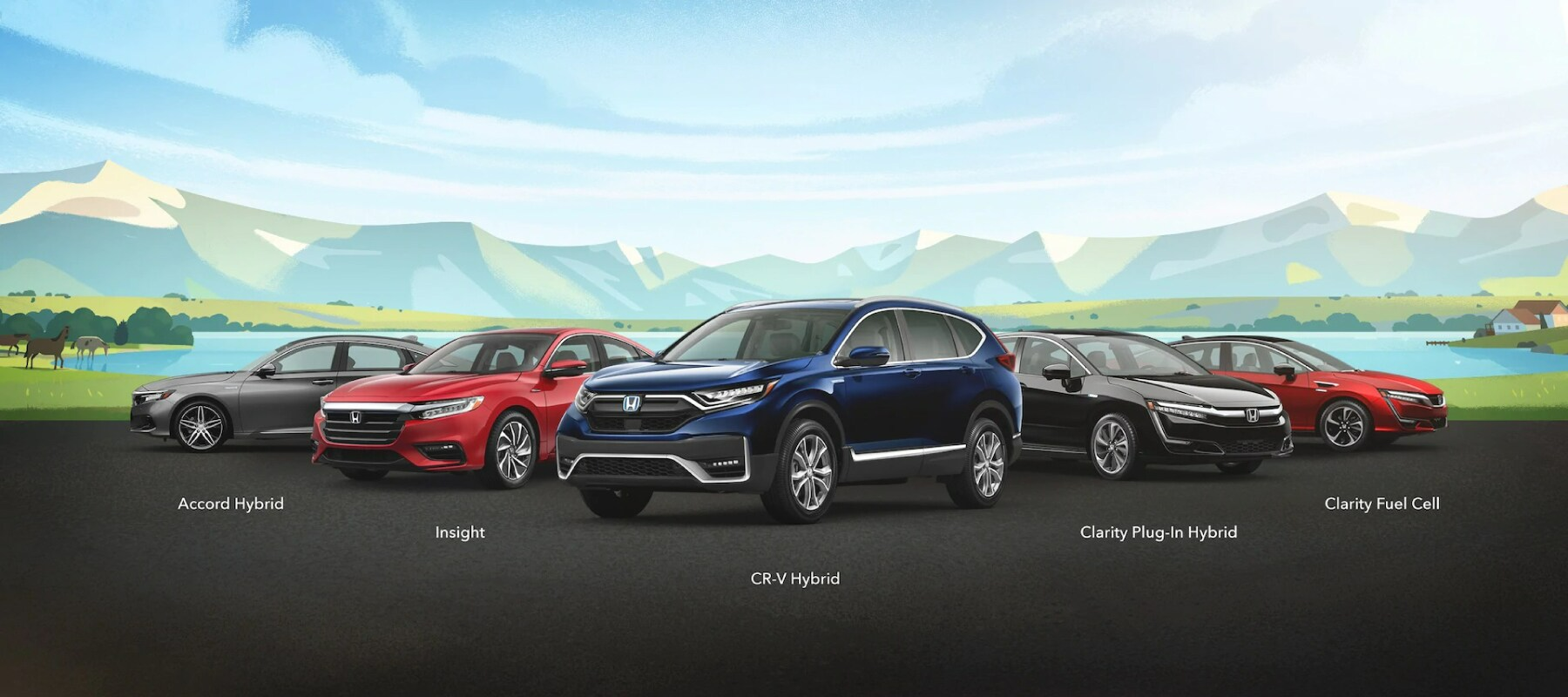

Electrified vehicles are for everyone.
Choose from a range of efficient, stylish and convenient options to find the right one for you.
2021 Honda Accord Hybrid shown in Modern Steel Metallic, 2021 Insight shown in Radiant Red Metallic, 2020 CR-V Hybrid shown in Obsidean Blue Pearl, 2021 Clarity Plug-In Hybrid shown in Crystal Black Pearl and 2021 Clarity Fuel Cell shown in Crimson Pearl (not available at Southeastern Honda).
Benefits of Electrified Vehicles
There are so many reasons to drive an electrified vehicle. These are just a few that can directly benefit you.

Fun to Drive
Instant torque* and impressive acceleration bring fun and excitement to driving electric vehicles.

Fill Up Less, Save More
Reduce or eliminate your reliance on gas and save money at the pump.

Incentives and Tax Credits
Potential benefits* include HOV lane access eligibility, lower electricity rates, a tax credit of up to $7,500* and more.

Low Emissions
A new electrified vehicle can help you feel good about your carbon footprint by reducing or eliminating your driving emissions.
There's One for Everyone
Whether you're commuting to work or heading out on a longer journey, there's an option that fits your lifestyle.

High-Voltage Battery Limited Warranty
Enjoy 8 years of high-voltage battery limited warranty coverage* on every Honda hybrid.
*Applies to all-electric and fuel-cell vehicles only. State incentives may vary. The IRS offers a Qualified Plug-In Electric Drive Motor Vehicle Tax Credit of up to $7,500 on the purchase of qualifying vehicles. This is not tax advice. Consult your own tax advisor for details. 8-year/100,000-mile warranty covers abnormal loss of capacity in the hybrid's high-voltage battery. Other warranties may provide additional coverage for the high-voltage battery. See dealer for details. High-voltage batteries degrade over time with use. Gradual capacity loss is expected and not covered under warranty.
Compare Electrified Technologies
Each electrified technology offers unique features and distinct advantages. Find the one that fits your lifestyle and driving needs.
Hybrid
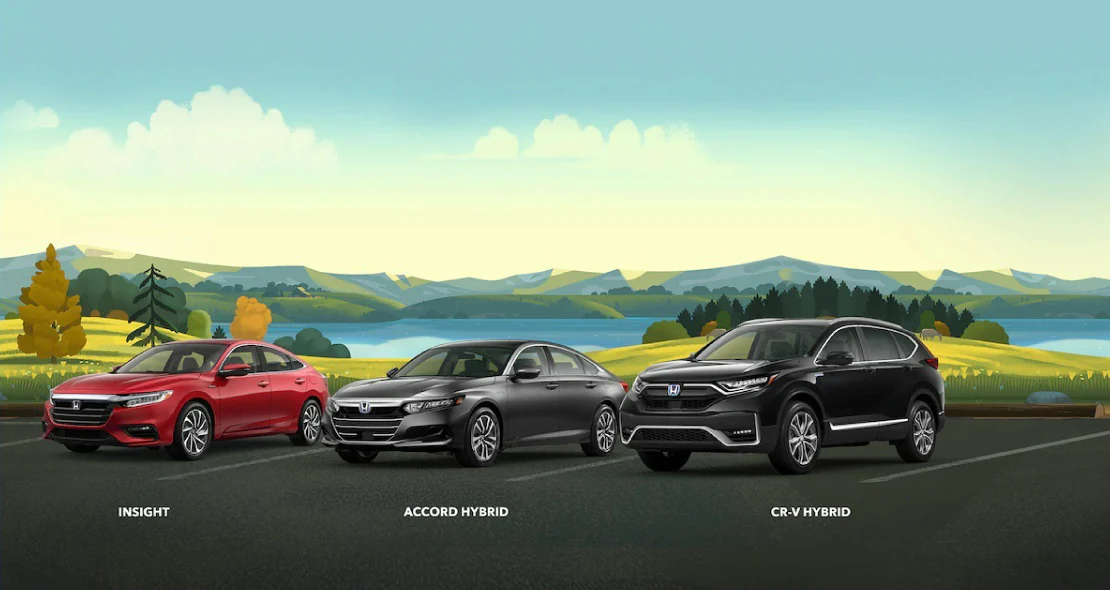

Unplugged and on the Road
Hybrid vehicles are more powerful and popular than ever. They never need to be plugged in, generate electricity while you brake and receive better mpg ratings, which may save money at the pump.* And now with stylish options like the Honda Insight, Accord Hybrid and CR-V Hybrid, they fit seamlessly into your lifestyle.
Plug-In Hybrid
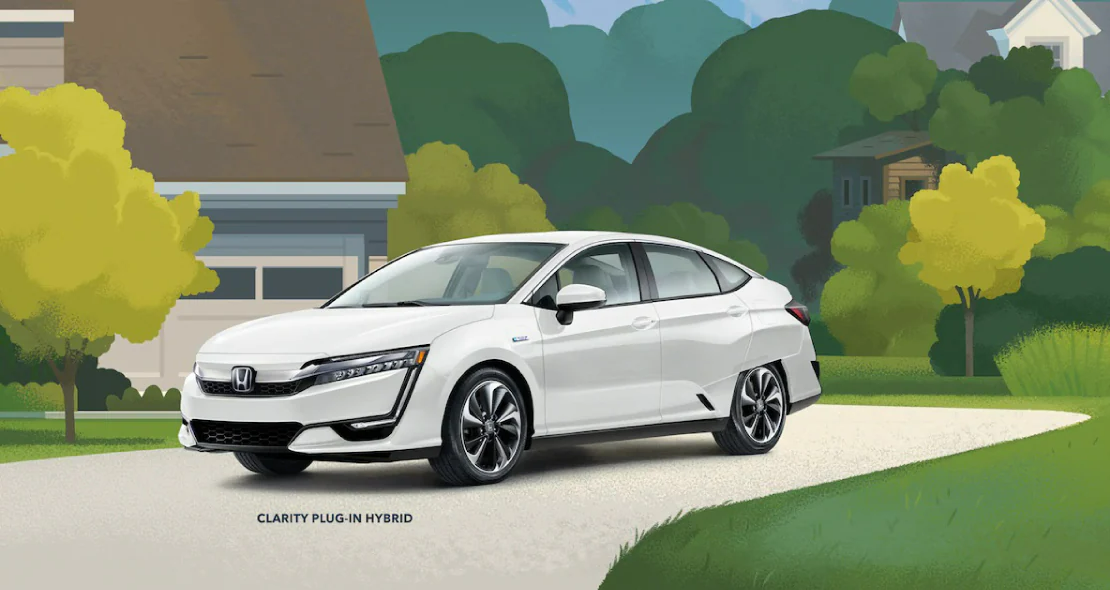

The Best of Both Worlds
Plug-in hybrids can function as all-electric, emission-free vehicles for short trips, then automatically switch to using a gas-powered engine when the battery runs low or when additional power is required. With the flexibility and peace of mind to go almost anywhere, vehicles like the Honda Clarity Plug-In Hybrid help you get the most out of your drive.
ENERGY SOURCE
Hybrid
- Runs on gas and electricity.
- Honda hybrids can recover lost energy through regenerative braking.
Plug-In Hybrid
- Runs on a store of electricity first, then automatically switches to gas when needed.
- Honda plug-in hybrids can recover lost energy through regenerative braking.
RECHARGING AND REFUELING
Hybrid
- Refuel at traditional gas stations.
- No plugging in or charging required.
Plug-In Hybrid
- Plugging in daily with convenient charging options is recommended to maximize electric usage.
- Gas is required.
BIGGEST ADVANTAGES
Hybrid
- Impressive mpg ratings and cost savings at the pump.
- Fewer stops at the gas station.
- Lower vehicle emissions than gasoline-only vehicles.
- No change of routine necessary.
Plug-In Hybrid
- Uses electricity for shorter drives and gas when needed, giving you peace of mind.
- Lower vehicle emissions than gasoline-only vehicles.
- No need to change your driving habits.
TYPES OF DRIVES
Hybrid
- Perfect for trips of any length.
Plug-In Hybrid
- Perfect for trips of any length.
- Short trips can be made using all-electric power.
Honda Batteries and Charging
Honda electrified vehicles are easy to charge and powered by batteries that are just as reliable as the vehicles themselves.
Designed for Longevity
Built to last and covered by long-term limited warranties, our high-voltage batteries provide a reliable and cost-effective experience.
The high-voltage lithium-ion batteries that power our electrified vehicles are designed for long-term use. They're covered by an 8-year/100,000-mile limited warranty*, which means less worrying about repair costs.
Our Commitment to Sustainability
We aim to have as little impact on the environment as possible by recycling materials from our batteries.
We harvest metals and components from our electrified-vehicle batteries whenever possible, and repurpose them in other products. This allows us to reuse valuable materials and reduce waste.
Easy Charging
Two convenient charging options make plugging in easy, whether you're at home or on the go.
Choose from two easy-to-use charging options for your Clarity Plug-In Hybrid: Level 1, which uses a household outlet*, and Level 2, a quicker charge at your home or at a charging station.
*8-year/100,000-mile warranty covers abnormal loss of capacity in the hybrid's high-voltage battery. Other warranties may provide additional coverage for the high-voltage battery. See dealer for details. High-voltage batteries degrade over time with use. Gradual capacity loss is expected and not covered under warranty. Honda recommends the use of a dedicated 120-volt GFCI outlet tested for use by an electrician.